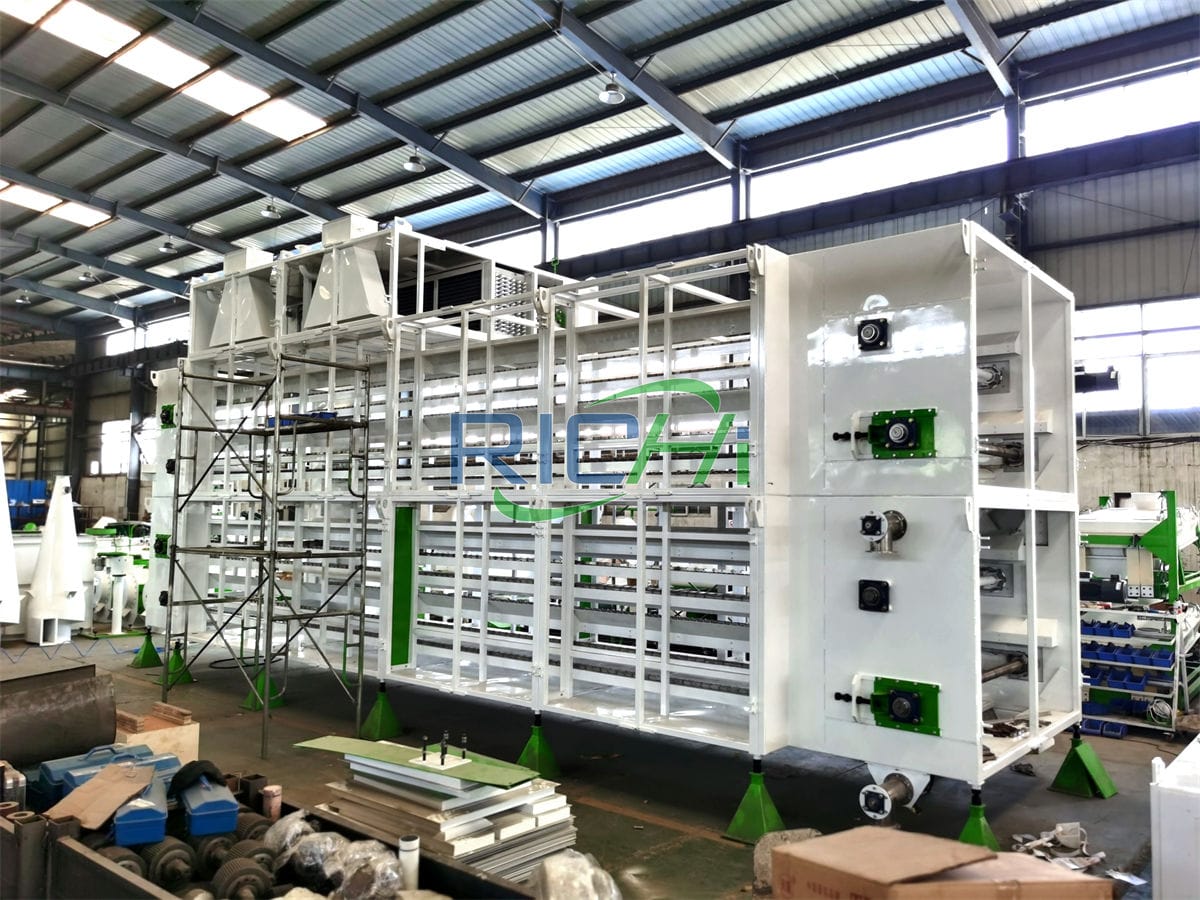
Setting up a 20 tons per hour (t/h) fish and poultry feed preparation plant requires a significant investment in various fixed assets. Understanding the primary cost components is essential for effective budgeting and financial planning. This article outlines the main cost items associated with establishing and operating a 20t/h feed preparation facility.
1. Equipment Costs
The core machinery and equipment constitute a significant portion of the initial investment. Key components include:
- Raw Material Handling Equipment:
- Silos and storage bins
- Conveying systems (screw conveyors, bucket elevators)
- Weighing and batching systems
- Grinding Equipment:
- Hammer mills or pulverizers
- Mixing Equipment:
- Horizontal or vertical mixers
- Conditioning and Extrusion Equipment:
- Steam conditioners
- Single or twin-screw extruders
- Drying and Cooling Equipment:
- Horizontal or vertical dryers
- Counterflow coolers
- Coating Equipment:
- Vacuum coaters for oil addition
- Packaging Equipment:
- Bagging machines
- Palletizers
Estimated Cost Range: $1,500,000 – $2,500,000
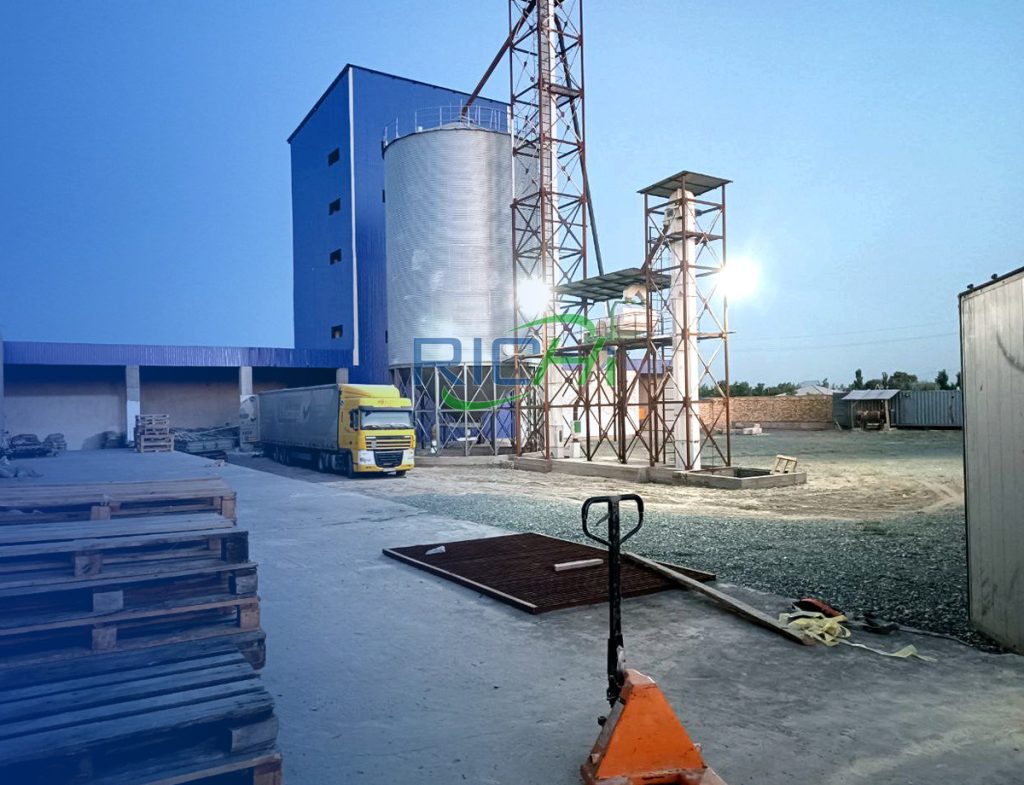

2. Building and Infrastructure
The facility requires adequate infrastructure, including:
- Factory Building Construction or Renovation:
- Foundations for heavy machinery
- Electrical installations and wiring
- Plumbing and water supply systems
- Ventilation and dust collection systems
- Office spaces and quality control laboratories
Estimated Cost Range: $500,000 – $1,000,000
3. Utility Setup and Operational Costs
Ongoing utility expenses are a significant aspect of operational costs:
- Electricity:
- Power for machinery operation
- Lighting and climate control
- Water:
- For conditioning and cleaning processes
- Steam Generation:
- Boilers for steam production used in conditioning
- Compressed Air Systems:
- For pneumatic controls and cleaning
Estimated Annual Cost: $200,000 – $400,000
4. Raw Material Costs
The largest ongoing expense in fish and poultry feed production includes:
- Fish meal and fish oil
- Plant-based proteins (soybean meal, wheat gluten)
- Grains and starches
- Vitamins and minerals
- Binders and additives
Estimated Annual Cost (at full capacity): $30,000,000 – $40,000,000
5. Labor Costs
Skilled personnel are necessary for various roles, including:
- Production operators
- Maintenance technicians
- Quality control staff
- Supervisors and management
- Administrative staff
Estimated Annual Cost: $500,000 – $800,000
6. Maintenance and Spare Parts
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal operation and includes:
- Routine maintenance supplies
- Replacement parts for wear items (dies, rollers, screens)
- Emergency repair services
Estimated Annual Cost: $150,000 – $250,000
7. Quality Control and Testing
Ensuring product quality is essential, involving:
- Laboratory equipment
- Testing supplies
- Third-party analysis services
Estimated Annual Cost: $100,000 – $200,000
8. Environmental Compliance and Waste Management
Meeting regulatory requirements involves:
- Dust collection and air filtration systems
- Wastewater treatment facilities
- Solid waste disposal
- Environmental permits and certifications
Estimated Initial Cost: $200,000 – $400,000
Estimated Annual Operational Cost: $50,000 – $100,000
9. Research and Development
Ongoing product improvement and innovation include:
- Formulation development
- Process optimization studies
- New product trials
Estimated Annual Cost: $100,000 – $300,000
10. Marketing and Sales
Promoting products and maintaining customer relationships involves:
- Marketing materials and campaigns
- Trade show participation
- Sales team expenses
- Customer support services
Estimated Annual Cost: $200,000 – $400,000
11. Insurance and Regulatory Compliance
Protecting the business and meeting legal requirements includes:
- Property and liability insurance
- Product liability insurance
- Regulatory compliance costs (FDA, USDA, etc.)
Estimated Annual Cost: $100,000 – $200,000
12. Logistics and Transportation
Moving raw materials and finished products involves:
- Inbound logistics for raw materials
- Outbound logistics for finished feed
- Fleet maintenance (if applicable)
- Third-party logistics services
Estimated Annual Cost: $500,000 – $1,000,000
13. Technology and Software
Managing operations and data involves:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system
- Manufacturing Execution System (MES)
- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Maintenance management software
Estimated Initial Cost: $100,000 – $300,000
Estimated Annual Operational Cost: $20,000 – $50,000
14. Training and Development
Ensuring staff competency and compliance involves:
- Initial training for new equipment and processes
- Ongoing skill development programs
- Safety training
- Compliance training
Estimated Annual Cost: $50,000 – $100,000
15. Financing Costs
If the project is financed through loans, consider:
- Interest payments
- Loan origination fees
- Varies based on loan terms and amount borrowed
Conclusion
The total initial investment for a 20t/h fish and poultry feed preparation plant can range from $3 million to $5 million, with annual operational costs (excluding raw materials) ranging from $2 million to $4 million. Raw material costs, which can exceed $30 million annually at full capacity, represent the largest ongoing expense.
When planning such a project, it’s essential to conduct a thorough market analysis to ensure demand for the production capacity. Additionally, careful consideration should be given to location, as it affects many cost factors, including labor, utilities, and logistics.
Effective management of these cost components is key to the profitability and success of a fish and poultry feed preparation plant. Implementing cost-saving measures, optimizing processes, and maintaining high product quality can help ensure the long-term viability of the operation in the competitive animal feed industry.
For details please contact: pellet plant
WhatsApp:86 138 3838 9622
Email:enquiry@richipelletmachine.com