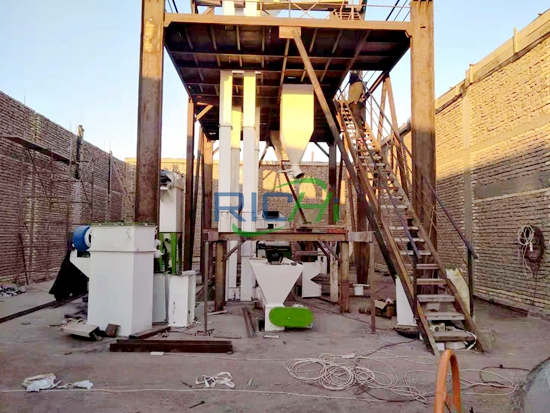
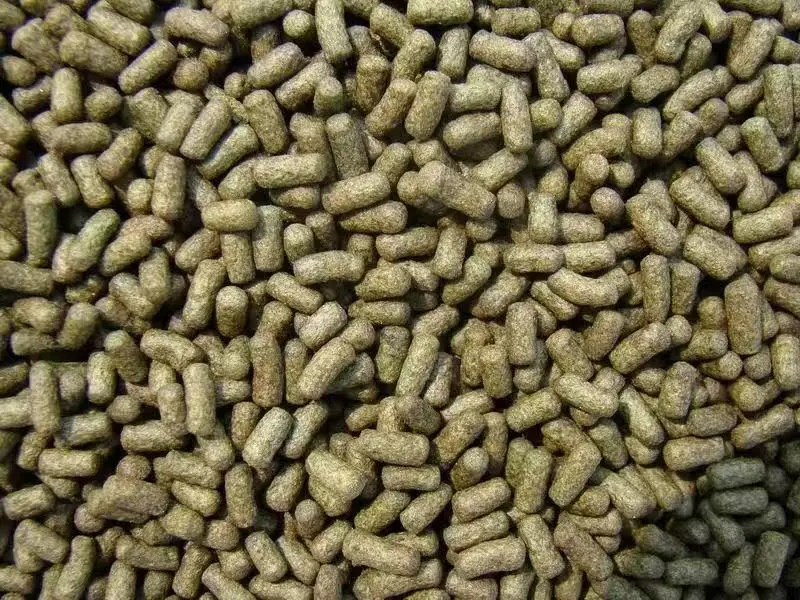
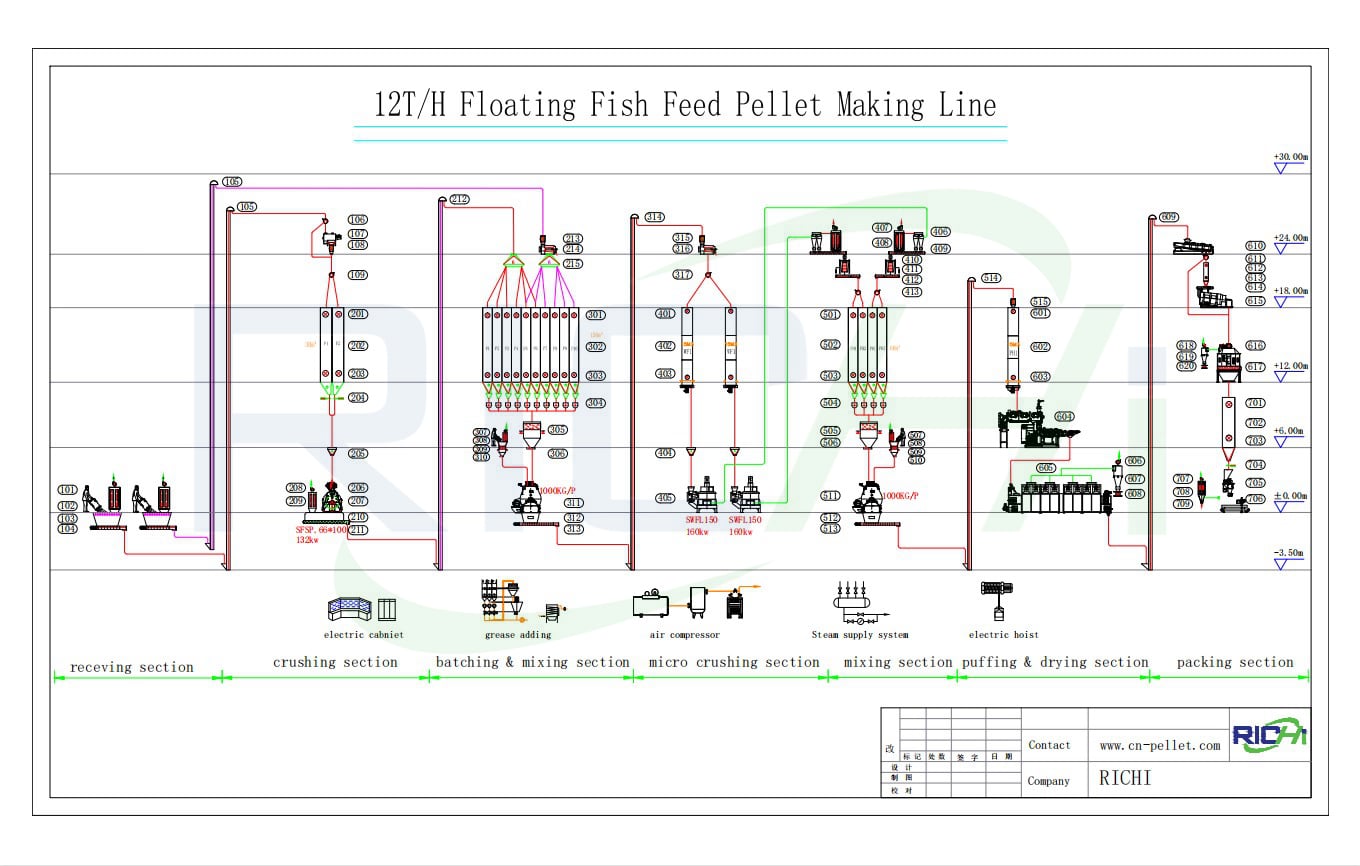
The production of fish feed pellets is a critical aspect of aquaculture, providing fish with the necessary nutrition for growth, health, and overall productivity. Fish feed pellet machines are designed to efficiently convert raw materials into pellets that meet the dietary needs of various fish species. The processing procedures involved in using a fish feed pellet machine are intricate and involve several stages, each of which plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and consistency of the final product. This article outlines the key processing procedures involved in the operation of a fish feed pellet machine. Fish feed processing line:
1. Raw Material Selection and Preparation
The first step in the fish feed processing line is the selection and preparation of raw materials. The quality and composition of these materials are fundamental to the nutritional value of the fish feed.
a. Ingredient Selection
Fish feed typically includes a variety of ingredients, such as fish meal, soybean meal, corn, wheat, vitamins, minerals, and additives. The choice of ingredients depends on the specific nutritional requirements of the fish species being cultivated. For instance, carnivorous fish may require a higher proportion of protein-rich ingredients like fish meal, while herbivorous species might require more plant-based components.
b. Grinding and Pulverizing
Once the raw materials are selected, they need to be ground and pulverized to achieve a uniform particle size. Grinding is a critical step because it affects the digestibility of the feed and the efficiency of the pelletizing process. A hammer mill or grinder is typically used to break down the raw materials into a fine powder. The finer the particle size, the better the binding and pellet formation during extrusion.
2. Mixing of Ingredients
After grinding, the different raw materials are thoroughly mixed to ensure that the nutrients are evenly distributed throughout the feed. This step is essential for maintaining the consistency and quality of the pellets.
a. Dry Mixing
In the dry mixing stage, the ground ingredients are blended together in a mixer. The goal is to achieve a homogeneous mixture where each pellet will contain a balanced amount of nutrients. Depending on the formulation, other dry additives like vitamins, minerals, and binders may also be incorporated during this stage.
b. Addition of Liquid Ingredients
In some cases, liquid ingredients such as oils, fats, or liquid binders are added to the mixture to enhance the nutritional content or improve the pelletizing process. The addition of liquids helps to improve the texture and cohesiveness of the pellets, ensuring that they remain intact during extrusion and drying.
3. Conditioning
Conditioning is a critical step that involves treating the mixed ingredients with steam or moisture before they are extruded into pellets. This process enhances the binding properties of the feed, improves the digestibility of the nutrients, and ensures the durability of the pellets.
a. Steam Conditioning
In steam conditioning, the mixed ingredients are exposed to steam, which raises the temperature and moisture content of the mixture. The heat and moisture help to soften the raw materials, making them more malleable and easier to shape into pellets. Conditioning also activates the natural binders in the ingredients, resulting in stronger, more cohesive pellets.
b. Temperature and Moisture Control
Precise control of temperature and moisture levels during conditioning is essential for producing high-quality pellets. If the mixture is too dry, the pellets may crumble and break apart. Conversely, if it is too wet, the pellets may become too soft and lose their shape. Modern fish feed pellet machines are equipped with advanced control systems that regulate the conditioning parameters to ensure optimal results.
4. Extrusion and Pelletizing
Extrusion is the core process in fish feed pellet production, where the conditioned mixture is forced through a die to form pellets. This stage involves several key operations that determine the size, shape, and quality of the final pellets.
a. Extrusion Process: price of fish feed extruder machine
During extrusion, the conditioned feed mixture is fed into an extruder, where it is subjected to high pressure and temperature. The mixture is pushed through a die with specific hole patterns that determine the size and shape of the pellets. The extrusion process causes the mixture to expand, which can produce floating pellets ideal for certain fish species. The pressure and temperature in the extruder also contribute to the gelatinization of starches in the feed, improving the digestibility and nutritional value of the pellets.
b. Pellet Cutting and Sizing
As the feed mixture exits the extruder, it is cut into pellets of the desired length by a rotating knife or cutter. The size of the pellets can be adjusted based on the requirements of the fish species being fed. Smaller pellets are suitable for juvenile fish, while larger pellets are used for adult fish. The cutting process must be precise to ensure uniform pellet size, which is important for consistent feeding and growth rates in fish.
5. Drying and Cooling
After extrusion, the freshly formed pellets contain a significant amount of moisture and heat, which must be removed to ensure the stability and shelf life of the feed. The drying and cooling processes are crucial for producing durable, stable pellets that can be stored and handled without degradation.
a. Drying Process
The drying process involves removing excess moisture from the pellets by passing them through a dryer or drying chamber. The dryer uses hot air to evaporate the moisture, reducing the water content of the pellets to an optimal level, usually around 10-12%. Proper drying is essential to prevent the growth of mold and bacteria, which can spoil the feed and harm the fish.
b. Cooling Process
Following drying, the pellets are cooled to ambient temperature using a cooling system. Cooling helps to solidify the pellets and remove any residual heat, making them more stable and less prone to damage during storage and transport. Rapid cooling is important to prevent the pellets from becoming too brittle, which can lead to breakage.
6. Screening and Packaging
The final steps in the fish feed pellet production process involve screening and packaging the finished pellets. These steps ensure that only high-quality pellets reach the end user, and they facilitate the efficient distribution and storage of the product.
a. Screening
Screening is the process of separating the finished pellets from any fines or broken pieces that may have resulted from the extrusion or drying process. A vibrating screen or sieve is typically used to remove these unwanted particles, ensuring that only uniform, intact pellets are packaged for distribution.
b. Packaging
Once the pellets have been screened, they are ready for packaging. The pellets are usually packed in bags or bulk containers that are labeled with relevant information, such as the pellet size, nutritional content, and expiration date. Proper packaging is essential for protecting the pellets from moisture, pests, and other environmental factors that could compromise their quality.
Conclusion
The fish feed processing lines are complex and involve multiple stages that must be carefully managed to produce high-quality fish feed. From the selection and preparation of raw materials to the extrusion, drying, and packaging of the final pellets, each step plays a critical role in ensuring that the feed meets the nutritional needs of fish and supports optimal growth and health in aquaculture operations. By understanding and optimizing these procedures, producers can achieve consistent, high-quality results that contribute to the success of their aquaculture ventures. More: RICHI Fish feed mill plant cost