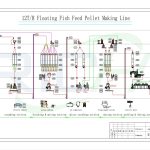
The Straw Pellet Production Line is a versatile system primarily designed to process straw into pellets. However, its adaptability allows for the production of various other types of biomass pellets. This versatility makes it a valuable asset for farmers, renewable energy producers, and businesses looking to diversify their product offerings or make use of different agricultural and forestry residues. Let’s explore the range of biomass types that can be produced using a Straw Pellet Production Line.
- Wood Sawdust Pellets
Many Straw Pellet Production Lines can effectively process wood sawdust into pellets. Sawdust, a byproduct of wood processing industries, can be transformed into high-density pellets suitable for:
- Residential heating
- Industrial boilers
- Power generation
Wood sawdust pellets are known for their high energy content and clean burning properties.
- Wood Chip Pellets
Similar to sawdust, wood chips from forestry operations or wood processing can be pelletized. These pellets are useful for:
- Large-scale heating systems
- Co-firing in power plants
- Industrial process heat
- Bamboo Waste Pellets
Bamboo processing waste, including leaves and small branches, can be effectively pelletized. Bamboo pellets offer:
- High calorific value
- Rapid renewability
- Low ash content
- Rice Husk Pellets
Rice husks, a byproduct of rice milling, can be processed into pellets. These pellets are valuable for:
- Biomass power plants
- Industrial heating
- As a soil amendment
- Corn Stalk Pellets
Corn stalks, often left as agricultural waste after harvesting, can be converted into energy-dense pellets. These are suitable for:
- Animal bedding
- Biomass fuel
- Soil amendment
- Soybean Stalk Pellets
Like corn stalks, soybean stalks can be pelletized to create a useful biomass product. These pellets can be used for:
- Livestock bedding
- Fuel in biomass boilers
- Organic mulch in agriculture
- Cotton Stalk Pellets
Cotton stalks, typically considered waste in cotton production, can be transformed into valuable pellets for:
- Industrial heating
- Power generation
- Soil improvement
- Sunflower Stalk Pellets
Sunflower stalks, often left in fields after harvest, can be processed into pellets. These are useful for:
- Residential heating
- Industrial boilers
- As a component in animal feed
- Peanut Shell Pellets
Peanut shells, a byproduct of peanut processing, can be effectively pelletized. These pellets are suitable for:
- Biomass fuel
- Animal bedding
- Organic fertilizer
- Grass Pellets
Various types of grass, including lawn clippings and dedicated energy crops like switchgrass, can be pelletized. Grass pellets are used for:
- Heating in pellet stoves
- Animal bedding
- Soil amendment
- Olive Pomace Pellets
In regions with olive oil production, olive pomace (the solid remains after oil extraction) can be pelletized. These pellets are valuable for:
- High-energy biomass fuel
- Organic fertilizer
- Soil conditioner
- Bagasse Pellets
Sugarcane bagasse, the fibrous matter that remains after sugarcane stalks are crushed to extract their juice, can be processed into pellets. Bagasse pellets are used for:
- Fuel in sugar mills
- Power generation
- As a renewable fuel source in various industries (Related post: Biomass Pellet Line)
- Coffee Husk Pellets
In coffee-producing regions, coffee husks can be pelletized. These pellets offer:
- A solution for coffee processing waste
- A renewable fuel source
- Potential use as organic fertilizer
- Coconut Shell Pellets
Coconut shells, often considered waste in coconut processing, can be turned into high-density pellets. These are valuable for:
- High-energy biomass fuel
- Activated carbon production
- As a component in landscaping materials
- Palm Kernel Shell (PKS) Pellets
In regions with palm oil production, palm kernel shells can be pelletized. PKS pellets are known for:
- High calorific value
- Low ash content
- Suitability for industrial heating and power generation
Advantages of Using Straw Pellet Production Line for Various Biomass
- Versatility: The ability to process a wide range of materials allows for adaptation to local agricultural and forestry conditions and available resources.
- Waste Reduction: Converting various agricultural and forestry residues into pellets helps in reducing waste and creating value from byproducts.
- Renewable Energy Production: Many of these biomass pellets serve as renewable energy sources, contributing to sustainable energy goals.
- Improved Material Handling: Pelletizing various biomass materials improves their density, making storage, transportation, and use more efficient.
- Market Diversification: The ability to produce different types of biomass pellets allows businesses to cater to various markets and applications.
- Year-Round Production: By processing different materials, the production line can operate throughout the year, maximizing equipment utilization.
Considerations for Producing Different Biomass TypesWhile the Straw Pellet Production Line is adaptable, some considerations are necessary when producing different biomass types:
- Die Specifications: Different materials may require changes in die specifications for optimal pellet formation.
- Moisture Content: Varying moisture levels in different biomass materials may necessitate adjustments in the drying or conditioning process.
- Grinding Requirements: Some materials may need finer or coarser grinding compared to straw for effective pelletization.
- Binding Properties: Certain biomass types might require the addition of natural binders to ensure pellet integrity.
- Energy Content Analysis: Regular testing is crucial to ensure that the pelletized biomass meets the intended energy content for its application.
- Ash Content Management: Different biomass types produce varying amounts of ash when burned, which may affect their suitability for certain applications.
Conclusion
The Straw Pellet Production Line demonstrates remarkable versatility in its ability to produce a wide range of biomass pellets. From agricultural residues to forestry byproducts, this production line offers the flexibility to create diverse biomass products tailored to different energy needs and local resource availability.
This adaptability not only maximizes the utility of the equipment but also provides opportunities for creating value-added products from what might otherwise be considered waste. By enabling the production of multiple biomass types, the Straw Pellet Production Line becomes a valuable tool in promoting circular economy principles and sustainable resource utilization.
As the demand for renewable energy sources and sustainable waste management solutions continues to grow, the versatility of equipment like the Straw Pellet Production Line will play an increasingly important role. It offers a practical solution for converting a wide array of biomass materials into standardized, easy-to-use pellets, contributing to both waste reduction and renewable energy production goals.