In the wood processing industry, drying is a crucial step that significantly impacts the quality and usability of the final product. Two common types of dryers used in this process are wood chip dryers and traditional dryers. While both serve the purpose of reducing moisture content, they differ in several key aspects. This article explores the main differences between wood chip dryers and traditional dryers, highlighting their unique features, advantages, and limitations.
- Design and Structure
Wood Chip Dryers:
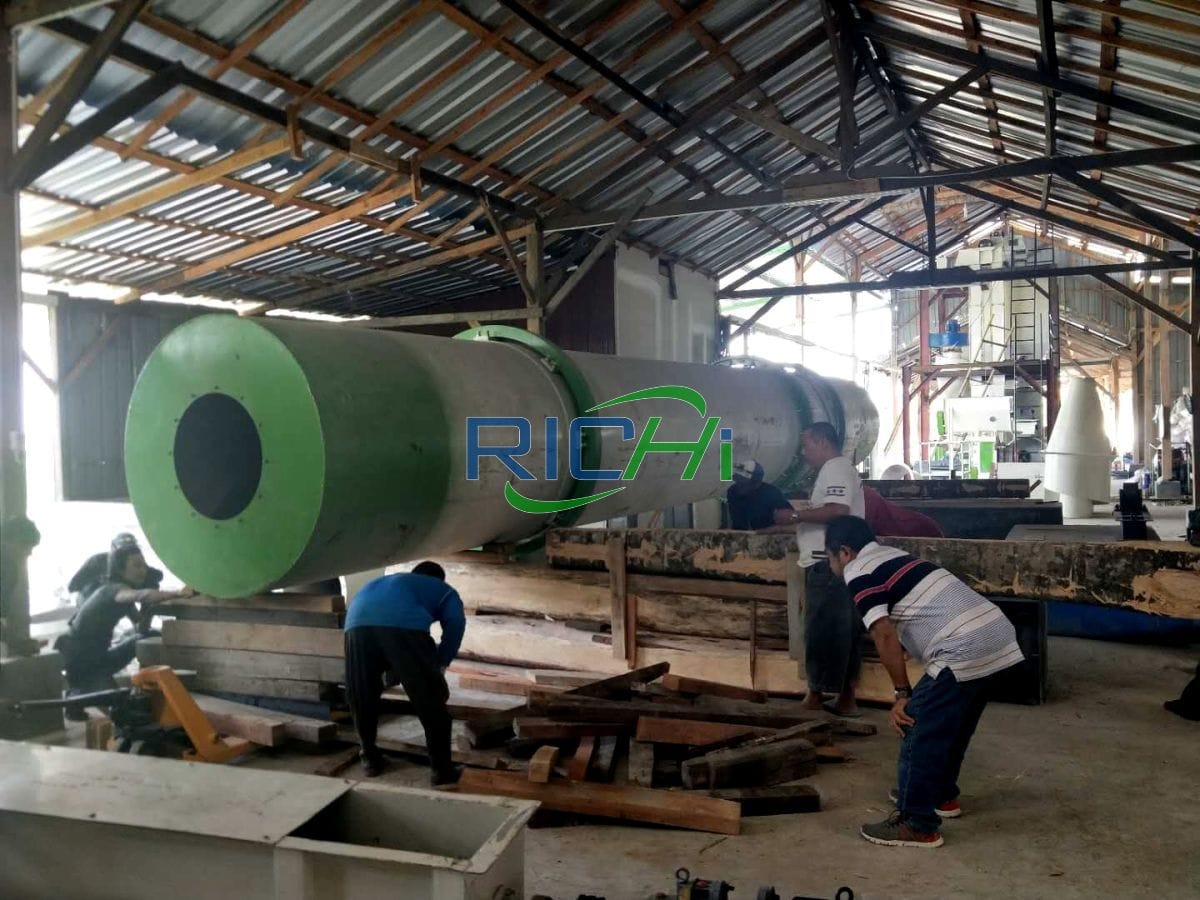
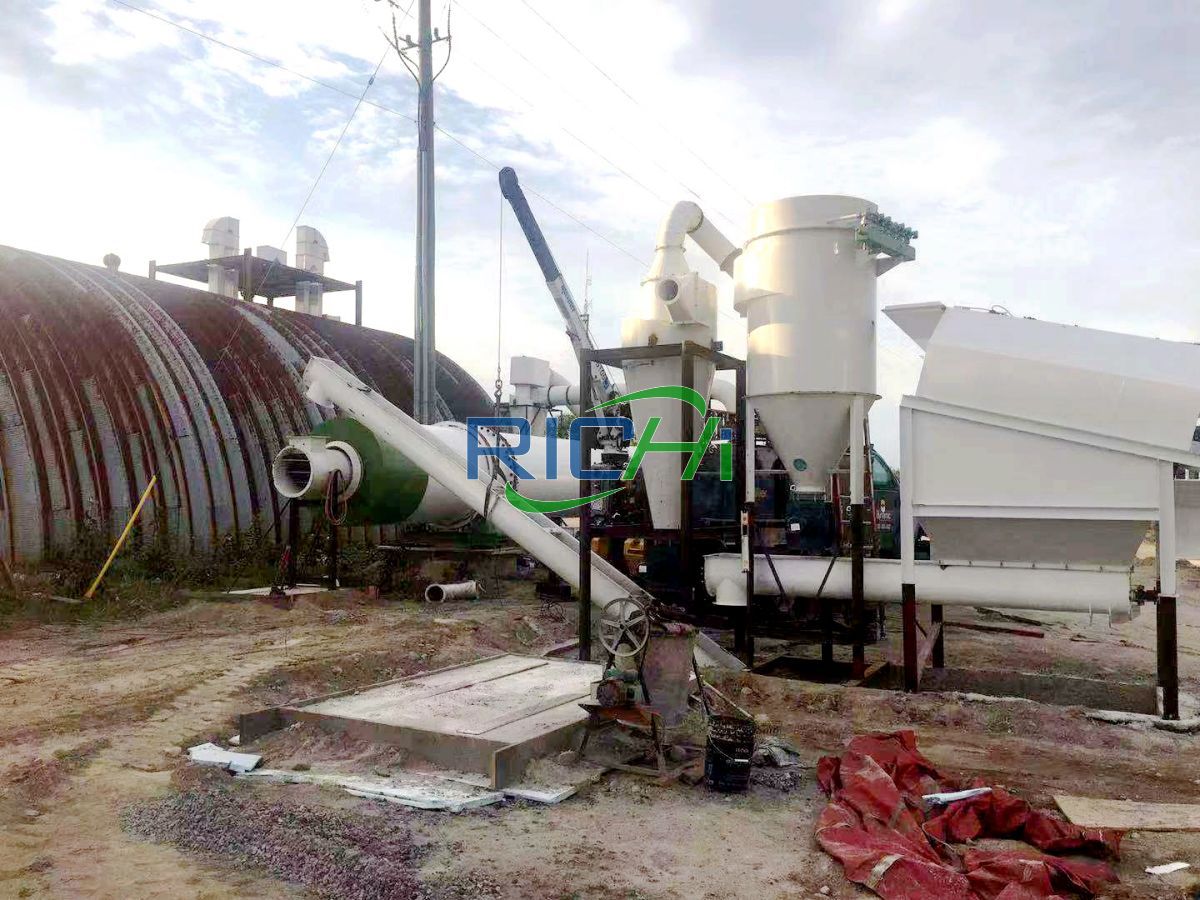
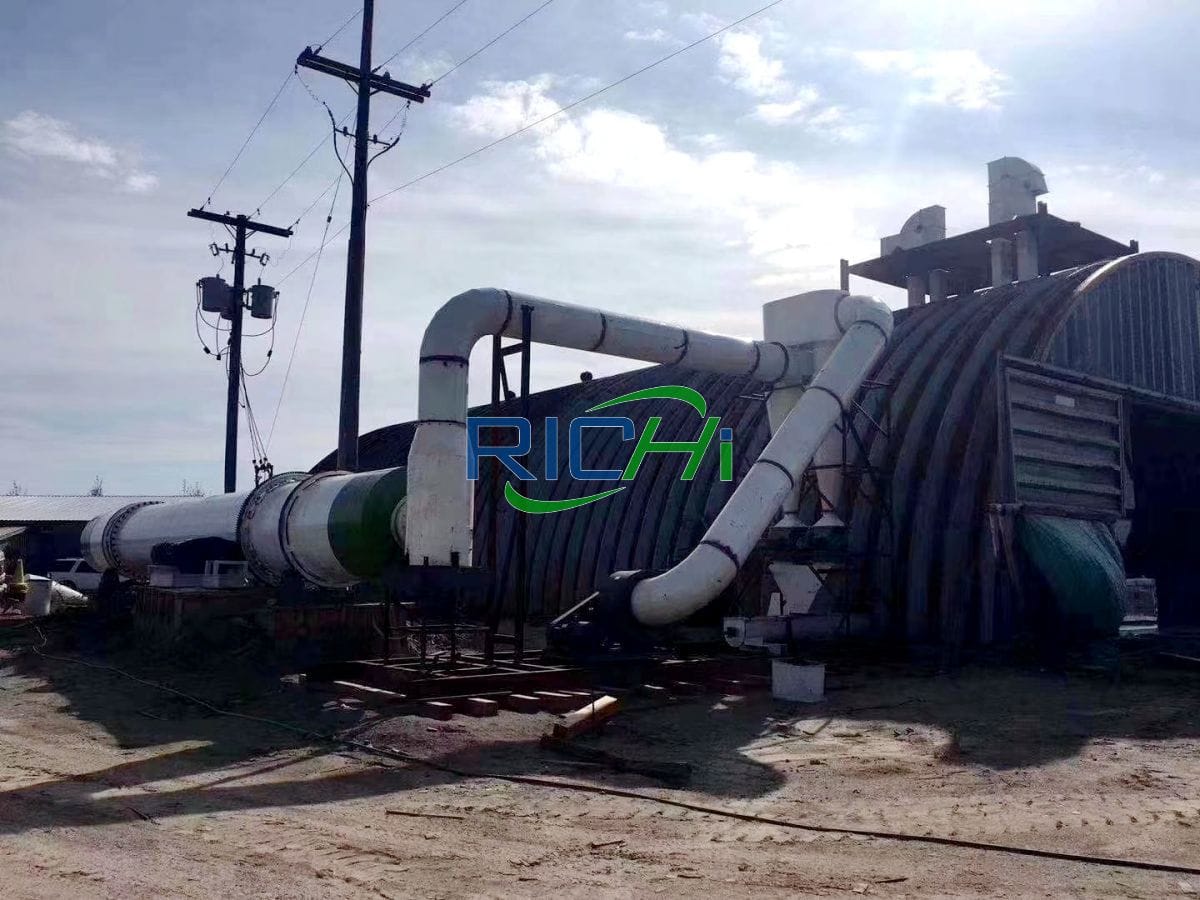
Wood chip dryers are specifically designed to handle wood chips, which are irregularly shaped and sized particles of wood. These dryers typically feature a rotating drum or a fluidized bed system. The rotating drum design allows for continuous tumbling of the wood chips, ensuring even drying. Fluidized bed systems use hot air to suspend and dry the chips, creating a fluid-like motion.
Traditional Dryers:
Traditional dryers, on the other hand, are more versatile and can handle a variety of materials, including sawdust, shavings, and larger wood pieces. They often use conveyor belt systems or stationary bed designs. These dryers may employ direct or indirect heating methods, depending on the specific application.
- Heating Method
Wood Chip Dryers:
Wood chip dryers primarily use direct heating methods. Hot air is typically generated by burning wood waste or other biomass fuels, making these dryers energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. The hot air is then circulated through the drying chamber, coming into direct contact with the wood chips.
Traditional Dryers:
Traditional dryers can use both direct and indirect heating methods. Direct heating is similar to wood chip dryers, while indirect heating uses heat exchangers to transfer heat to the drying chamber without direct contact between the heat source and the material being dried. This method is often preferred for materials sensitive to contamination or when precise temperature control is required.
- Drying Efficiency
Wood Chip Dryers:
Due to their specialized design, wood chip dryers are highly efficient in drying wood chips. The tumbling action in drum dryers or the fluidization in bed systems ensures that all surfaces of the chips are exposed to the hot air, resulting in uniform drying. This efficiency allows for faster drying times and higher throughput.
Traditional Dryers:
Traditional dryers can be efficient for a wide range of materials but may not match the specific efficiency of wood chip dryers when it comes to drying wood chips. The efficiency can vary depending on the design and the material being dried. For materials other than wood chips, traditional dryers may offer better performance. (Related post:horizontal dryer)
- Capacity and Throughput
Wood Chip Dryers:
Wood chip dryers are designed to handle large volumes of wood chips continuously. They can process several tons of wood chips per hour, making them suitable for industrial-scale operations. The continuous flow design allows for high throughput and consistent production.
Traditional Dryers:
The capacity of traditional dryers can vary widely depending on their design and intended use. While some industrial-scale traditional dryers can match the throughput of wood chip dryers, others are designed for smaller-scale operations or batch processing. This versatility makes traditional dryers suitable for a wider range of applications and production scales.
- Energy Consumption
Wood Chip Dryers:
Wood chip dryers are often more energy-efficient when it comes to drying wood chips. Many models are designed to use wood waste as fuel, creating a closed-loop system that reduces overall energy costs. The direct heating method also contributes to energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss.
Traditional Dryers:
The energy consumption of traditional dryers can vary depending on the heating method and design. While some modern traditional dryers are highly energy-efficient, others may consume more energy, especially if they use indirect heating methods or are not optimized for the specific material being dried.
- Temperature Control and Uniformity
Wood Chip Dryers:
Wood chip dryers typically offer good temperature control and uniformity due to their specialized design. The continuous movement of chips ensures even exposure to heat, resulting in consistent moisture content across the batch.
Traditional Dryers:
Temperature control in traditional dryers can be more precise, especially in indirect heating systems. This makes them suitable for materials that require exact temperature profiles during drying. However, achieving uniform drying can be more challenging, especially for large or irregularly shaped materials.
- Flexibility and Adaptability
Wood Chip Dryers:
While highly efficient for wood chips, these dryers are less flexible when it comes to drying other materials. They are optimized for a specific particle size and shape, which limits their versatility.
Traditional Dryers:
Traditional dryers offer greater flexibility and can be adapted to dry a wide range of materials. This adaptability makes them suitable for operations that process various types of wood products or other materials.
- Maintenance and Operational Complexity
Wood Chip Dryers:
Wood chip dryers, being specialized equipment, may require specific maintenance procedures. However, their design is often straightforward, focusing on the efficient drying of wood chips, which can simplify operational requirements.
Traditional Dryers:
The maintenance and operational complexity of traditional dryers can vary widely depending on their design and features. Some may be simple to operate and maintain, while others, especially those with advanced control systems, may require more specialized knowledge and maintenance procedures.
- Environmental Impact
Wood Chip Dryers:
When using wood waste as fuel, wood chip dryers can have a lower environmental impact. They often operate in a closed-loop system, utilizing waste products from wood processing as an energy source, which reduces overall emissions and waste.
Traditional Dryers:
The environmental impact of traditional dryers depends on their energy source and efficiency. While some modern traditional dryers are designed with environmental considerations in mind, others may have a higher carbon footprint, especially if they rely on fossil fuels for heating.
Conclusion
Both wood chip dryers and traditional dryers have their place in the wood processing industry. Wood chip dryers excel in efficiently drying large volumes of wood chips, offering high throughput and energy efficiency for this specific application. Traditional dryers, on the other hand, provide greater versatility and adaptability, making them suitable for a wider range of materials and production scales.
The choice between a wood chip dryer and a traditional dryer depends on factors such as the primary material being dried, production volume, energy considerations, and the need for flexibility in processing different materials. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with specific operational needs and environmental goals in the wood processing industry.
For details please contact: wood pellet making machine
WhatsApp:86 138 3838 9622
Email:enquiry@richipelletmachine.com